- 07.10.2024
- Menstrual Cycle Basics
What is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is defined as the time from the first day of one period to the first day of the next. It typically lasts between 21 to 35 days, with an average of 28 days. Each cycle involves complex hormonal changes that prepare the body for a potential pregnancy.
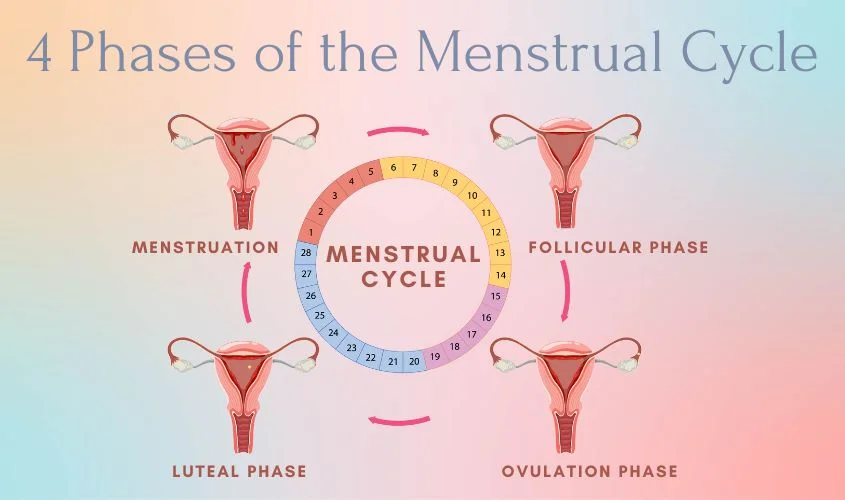
The 4 Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
1. Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5)
The first phase of the menstrual cycle is the menstrual phase, which starts on the first day of your period. During this phase, the uterine lining, which thickened in anticipation of a fertilized egg, is shed through menstruation. This phase usually lasts between 3 to 7 days.
Key Symptoms:
- Cramping and bloating
- Mood swings
- Fatigue
- Breast tenderness
Tracking Your Menstrual Phase:
To track your menstrual phase, mark the first day of your period on a calendar. Note any symptoms you experience, as this information can be helpful for future cycles.
2. Follicular Phase (Days 1-13)
The follicular phase overlaps with the menstrual phase, starting on the first day of menstruation and lasting until ovulation. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to develop follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg, and one follicle will eventually mature into an egg ready for ovulation.
Key Symptoms:
- Increased energy levels
- Thicker cervical mucus
- Changes in libido
Tracking Your Follicular Phase:
To track the follicular phase, observe changes in your cervical mucus, which becomes clearer and more slippery as ovulation approaches. You may also notice a boost in energy levels during this phase.
3. Ovulation Phase (Day 14)
The ovulation phase typically occurs around the middle of the cycle, usually around day 14 in a 28-day cycle. During this phase, a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of a mature egg from the dominant follicle in the ovary. The egg travels down the fallopian tube, where it can meet sperm for fertilization.
Key Symptoms:
- Mild cramping on one side
- Increased libido
- Changes in cervical mucus (clear and stretchy)
- Ovulation spotting (in some cases)
Tracking Your Ovulation Phase:
To track ovulation, pay attention to your body’s signs, such as changes in cervical mucus and basal body temperature. Many people use ovulation predictor kits to identify the LH surge.
4. Luteal Phase (Days 15-28)
The final phase of the menstrual cycle is the luteal phase, which occurs after ovulation and lasts until the start of your next period. During this phase, the empty follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This hormone helps thicken the uterine lining, preparing it for a potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
If fertilization does not occur, hormone levels drop, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining and the start of a new menstrual cycle.
Key Symptoms:
- PMS symptoms (mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness)
- Fatigue
- Changes in appetite
- Headaches
Tracking Your Luteal Phase:
To track the luteal phase, note any premenstrual symptoms you experience. You can also monitor your basal body temperature, which may remain elevated during this phase.
Why Understanding the Phases is Important
Knowing the four phases of your menstrual cycle can help you:
- Track Your Period: By understanding the phases, you can predict when your next period will start and how long it will last.
- Manage Symptoms: Recognizing which phase you’re in can help you prepare for symptoms like cramping or mood swings.
- Plan for Pregnancy: If you’re trying to conceive, tracking your ovulation phase can increase your chances of becoming pregnant.
- Identify Irregularities: If your cycle deviates significantly from the norm, understanding the phases can help you identify potential issues to discuss with your healthcare provider.
Tips for Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle
- Use a Calendar or App: Mark the start and end dates of your periods on a calendar or use a menstrual tracking app like Selin. These tools can help you identify patterns in your cycle.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep a record of any symptoms you experience throughout each phase. This information can help you understand your cycle better.
- Be Consistent: Track your cycle for several months to gain a comprehensive understanding of its patterns.
Conclusion
The menstrual cycle consists of four distinct phases: menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal. Understanding these phases can empower you to manage your reproductive health, plan for pregnancy, and track your cycle effectively. By being aware of your body’s changes, you can navigate your menstrual cycle with confidence.
Start Tracking Your Cycle with Selin
To stay on top of your menstrual cycle, download the Selin app today! With features that help you track your period, symptoms, and fertility, you can take control of your reproductive health effortlessly. Whether you’re looking to prepare for your next period or planning for pregnancy, the Selin app is your perfect companion.
Understanding the menstrual cycle is essential, and for insights into the common symptoms you might experience during each phase, check out our Menstrual Symptoms article.














